Publications
Estimates of the isotope effect for Nitrate assimilation in the Indian Sector of the Southern Ocean
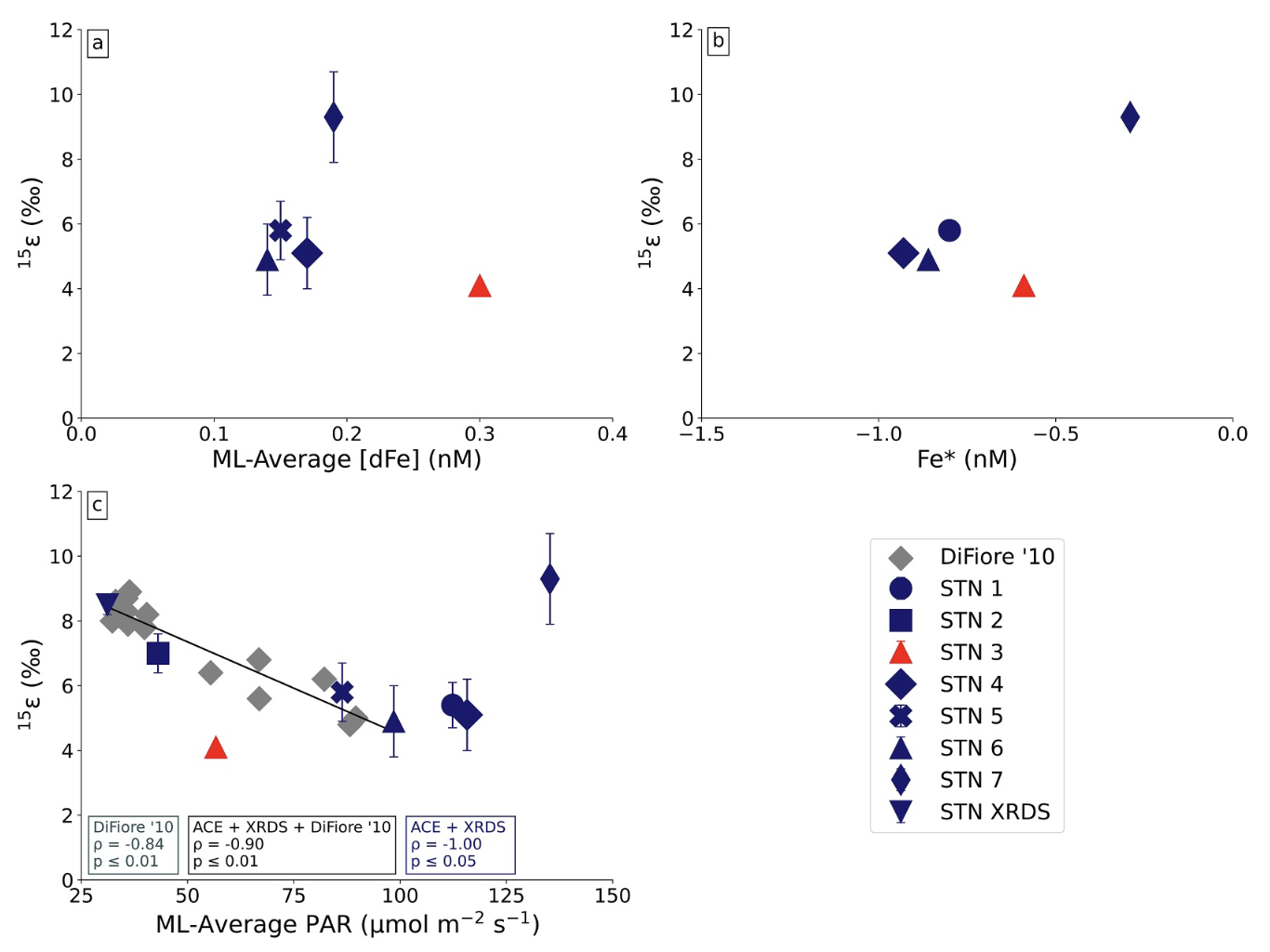
Utilising nitrate isotopic compositions to investigate phytoplankton nitrate consumption dynamics - a process with implications for current and paleo ocean carbon export - suggests that light, rather than iron availability or phytoplankton community composition, primarily influences uptake dynamics.
Key findings:
Nitrate assimilation isotope effects are estimated for the Indian sector of the Subantarctic and Antarctic regions of the Southern Ocean
Nitrate assimilation isotope effects increase with decreasing average mixed layer PAR flux within an optimal range
Dual nitrate isotopic composition profiles showed evidence of significant summertime nitrification on the Kerguelen Plateau
Thomas, R. K., Fawcett, S. E., Forrer, H. J., Robinson, C. M., & Knapp, A. N. (2024). Estimates of the isotope effect for Nitrate assimilation in the Indian Sector of the Southern Ocean. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 129(7), e2023JC020830.
A circum‐Antarctic plankton isoscape: Carbon export potential across the summertime southern ocean
Assessing carbon export across the circumpolar Southern Ocean using a two-endmember isotope mixing model, we find a higher than expected fraction of summertime productivity being exported, suggesting previous underestimations of carbon export.
Key findings:
Phytoplankton community composition influences suspended particulate matter carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios across the Southern Ocean
The nitrogen isotopes of particulate matter and a two-endmember isotope mixing model can be used to estimate carbon export potential
40% of summertime primary production is potentially exported, with a higher fraction exported near (Sub)Antarctic islands and melting ice
Stirnimann, L., Bornman, T. G., Forrer, H. J., Mirkin, J., Ryan‐Keogh, T. J., Flynn, R. F., ... & Fawcett, S. E. (2024). A circum‐Antarctic plankton isoscape: Carbon export potential across the summertime southern ocean. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 38(1), e2023GB007808.
Quantifying N₂ fixation and its contribution to export production near the Tonga-Kermadec Arc using nitrogen isotope budgets
Using a nitrogen budget to assess impacts of shallow hydrothermal vents on carbon export, we find regional export was supported by increased nitrogen fixation - an unexpected driver of carbon export.
Key findings:
Iron supply from shallow hydrothermal vents support high rates of N₂ fixation
High 15N₂ uptake rate estimates associated with Trichodesmium spp.
N₂ fixation supports 64 to 92% of export production in the late spring
Tonga-Kermadec Arc is a region of elevated carbon export that was previously overlooked
Forrer, H. J., Bonnet, S., Thomas, R. K., Grosso, O., Guieu, C., & Knapp, A. N. (2023). Quantifying N2 fixation and its contribution to export production near the Tonga-Kermadec Arc using nitrogen isotope budgets. Frontiers in Marine Science, 10, 1249115.
Natural iron fertilization by shallow hydrothermal sources fuels diazotroph blooms in the ocean
This large, collaborative effort shows that hydrothermal vent activity can ultimately supply enough iron to the surface to support a strong biological response.
Key findings:
Hydrothermal iron fertilization in the Tonga region boosts biological productivity and carbon sequestration by enhancing the growth of nitrogen-fixing Trichodesmium.
Diazotroph activity in this region is two to eight times higher than in nearby areas, contributing about 21% of global oceanic nitrogen fixation.
The discovery of this iron source highlights a crucial, previously unrecognized mechanism that may amplify oceanic CO₂ uptake as the climate warms.
Bonnet, S., Guieu, C., Taillandier, V., Boulart, C., Bouruet-Aubertot, P., Gazeau, F., ... Forrer, H. J, …& Tilliette, C. (2023). Natural iron fertilization by shallow hydrothermal sources fuels diazotroph blooms in the ocean. Science, 380(6647), 812-817.
The influence of Agulhas leakage on primary production and nitrogen cycling in the southeastern Atlantic Ocean
Assessing Agulhas Current “leakage” (eddies) and the impact on carbon sequestration, we find nitrification (conversion of ammonium to nitrate) occurring within the eddies to be the dominant nutrient supply to phytoplankton, decreasing carbon export potential in the region.
Key findings:
Primary production and carbon export potential are elevated at Agulhas eddy edges and reduced at their centers
Agulhas eddies host high rates of mixed-layer nitrification that can supply 100% of phytoplankton nitrate
Dissolved organic nitrogen appears to fuel a significant fraction of primary production in Agulhas eddies and the Cape Basin
Wallschuss, S., Mdutyana, M., Parrott, R. G., Forrer, H. J., Roman, R., Walker, D. R., ... & Fawcett, S. E. (2022). The influence of Agulhas leakage on primary production and nitrogen cycling in the southeastern Atlantic Ocean. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 127(9), e2022JC018971.
A global ocean dissolved organic phosphorus concentration database (DOPv2021)
Dissolved organic phosphorus (DOP) plays a key role in marine biogeochemical processes like nitrogen fixation and primary production. This new database compiles over 3,800 surface ocean observations from 1990–2021 across all major ocean basins, offering valuable insights for ocean nutrient cycling research.
Key offerings:
Includes the poorly represented Indian, South Pacific, and Southern Oceans and provides insight into spatial distributions of DOP in the ocean.
Valuable for researchers who work on marine primary production and nitrogen fixation.
Liang, Z., McCabe, K., Fawcett, S. E., Forrer, H. J., Hashihama, F., Jeandel, C., ... & Knapp, A. N. (2022). A global ocean dissolved organic phosphorus concentration database (DOPv2021). Scientific Data, 9(1), 772.
Exploring the coupled ocean and atmosphere system with a data science approach applied to observations from the Antarctic Circumnavigation Expedition
Using a novel approach: applying machine learning to 111 Southern Ocean variables, identifying temporal patterns of ocean–atmosphere interactions across physical, chemical, and biological processes, work at this scale remains unique.
Key findings:
Oceanic circulation patterns, frontal systems, and proximity to islands were shown to significantly influence nutrient availability, shaping microbial community structure and biological productivity. These features act as biogeochemical hotspots, underlining their central role in regulating ecosystem processes in the Southern Ocean.
Sea ice was associated with increased phytoplankton growth and net community productivity, likely due to iron fertilization and reduced light limitation. Additionally, sea ice influenced salinity and wave damping, making it a key driver in both physical and biological ocean dynamics.
Clear regional patterns in aerosol characteristics emerged, driven by sea state, atmospheric processing, and local source processes. These aerosol dynamics directly affect cloud condensation nuclei availability and, thus, cloud formation, emphasizing the need for climate models to accurately represent such ocean–atmosphere interactions.
Landwehr, S., Volpi, M., Haumann, F. A., Robinson, C. M., Thurnherr, I., Ferracci, V., ...Forrer, H.J.,… & Schmale, J. (2021). Exploring the coupled ocean and atmosphere system with a data science approach applied to observations from the Antarctic Circumnavigation Expedition. Earth System Dynamics, 12(4), 1295-1369.